1. To what extent do Chicago Public School (CPS) schools use exclusionary disciplinary practices, including out-of-school suspensions, in-school suspensions, and police notifications/arrests?
2. Have Chicago schools changed their use of exclusionary disciplinary practices from 2008-09 to 2013-14, particularly in years when district policy changes occurred?
3. What are the differences in suspension rates across different groups of students (by race, gender, achievement level, and disability status)?
4. Why do students receive exclusionary discipline? What types of incidents are most prevalent in schools?
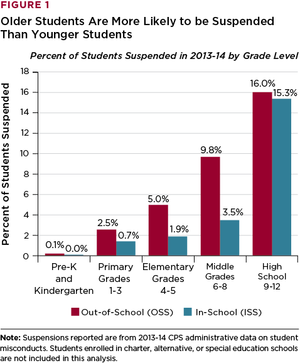
Suspension rates in CPS have declined markedly but still remain very high, particularly among the system’s most vulnerable students. In the 2013-14 school year, 16 percent of CPS high school students received an out-of-school suspension (OSS), down from 23 percent in 2008-9. Still, 24 percent of high school students with an identified disability and 27 percent of high school students in the bottom quartile of achievement received out-of-school suspensions in 2013-14. Suspension rates for Black boys in high school remain particularly high, with one-third receiving at least one out-of-school suspension.
This report finds that at the same time out-of-school suspension rates have declined, students and teachers across the district report feeling safer. At the high school level, student perceptions of safety and teacher perceptions of order have been improving since the 2008-09 school year; this is also the period during which OSS rates declined in high schools.
The report tracks suspension and arrest rates in Chicago schools over a six-year period, as CPS implemented a number of policies intended to improve school climate and reduce the amount of instructional time lost to suspensions. The policies are part of a larger national push to move away from “zero-tolerance” discipline policies and reduce the use of practices that remove students from the classroom. A follow-up report will examine more closely the relationship between reductions in suspensions and school climate, particularly in schools that had the highest suspension rates.
Key findings from the report include:
- Suspension rates are strongly related to students’ prior test scores, their race, and their gender. Black students are much more likely to be suspended than students of other races/ethnicities. Suspension rates are particularly high for Black boys in high school. About one-third of Black boys in high school (33 percent) received an OSS in 2013-14. In comparison, 13 percent of Latino boys in high school and 6 percent of White/Asian high school boys received an OSS in 2013-14. Black girls also have high OSS rates in high school, at 23 percent in 2013-14. This compares to high school OSS rates of 6 percent for Latina girls and 2 percent for White/Asian girls.
- Students with low entering test scores are also much more likely to be suspended, and lose instructional time, than those who begin the year with high test scores. In high school, 7 percent of students with the highest test scores received an OSS in the 2013-14 school year. In contrast, about a quarter of high school students with the lowest incoming test scores received an OSS.
- The decline in high school OSS rates has been accompanied by a doubling of in-school suspension (ISS) rates among Black high school students. In the 2013-14 school year, 15 percent of high school students received at least one in-school suspension, up from 11 percent in 2008-09. Thus, the rise in in-school suspensions is counter-balancing the decline in out-of-school suspensions. In-school suspensions are given more frequently to Black students than students of other racial/ethnic groups. ISS rates nearly doubled for Black high school students between 2008-09 and 2013-14, but remained the same for other student groups.
- Most suspensions in high schools result from acts of student defiance rather than violence or illegal behavior. At the high school level, about 60 percent of out-of-school suspensions and almost all in-school suspensions result from defiance of school staff, disruptive behaviors, and school rule violations. While administrators interviewed for the study recognized fights as a primary concern in their schools, 27 percent of out-of-school and 7 percent of in-school suspensions in high school are for physical conflict or threats to safety. Most suspensions result from conflicts that involve no physical harm.