Key Questions
1. What role does skill-based sorting plays in shaping students’ academic achievement, given a common curriculum for all students?
Overview
How students are sorted into classrooms by skill level can have as much of an effect on their achievement as the content they are taught.
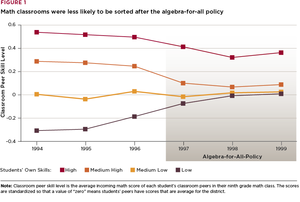
This study examines the effects of two curricular reforms by Chicago Public Schools, one that sorted students into algebra classes based on skill level and another that de-sorted students.
Key findings from the report include:
- Overall, test scores improve when students are sorted by skill level. Low-skilled students have slightly lower test scores with sorting, while high-skilled students have substantially higher test scores.
- The grades and pass rates of high-skilled students decline, while the grades of low-skilled students improve.
- When classes are sorted by skill level, low-skilled students are at higher risk of being in disruptive classrooms and thus, weaker instructional environments. Teachers in these classrooms need support around classroom management and getting students engaged in challenging work.
Publication Tags